Object Oriented Programming Concepts Explained
Put simply, object oriented programming is the use of objects that contain both data and methods that interact with each other. For a language to be considered object oriented, it must have certain features like:
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
These features, along with a language having Objects and Classes, make up what we know as object oriented programming.
What is Encapsulation
Encapsulation is achieved when an object keeps its state private, so other objects don't have direct access to this state. Instead they must call a list of public methods to manipulate the state.
Take the photo below for example. The Cat has 3 different fields that are all private, plus a private meow() method. No other object that calls the Cat can change these values.
However, the Cat also has a list of public methods(Sleep, Play, and Feed). These public methods when called, will change the Cat's state as well as invoke the meow() method for Play and Feed.
What is Inheritance
Inheritance is the creation of a hierarchy within your classes. You start off with a parent class, and then extend onto child classes which will reuse all of the fields and methods from the parent class plus any unique methods it implements.
Like the example below, the Teacher and the Student are both Person's, but one has a subject while the other has a school. Person is the parent class and Teacher & Student are the child classes.
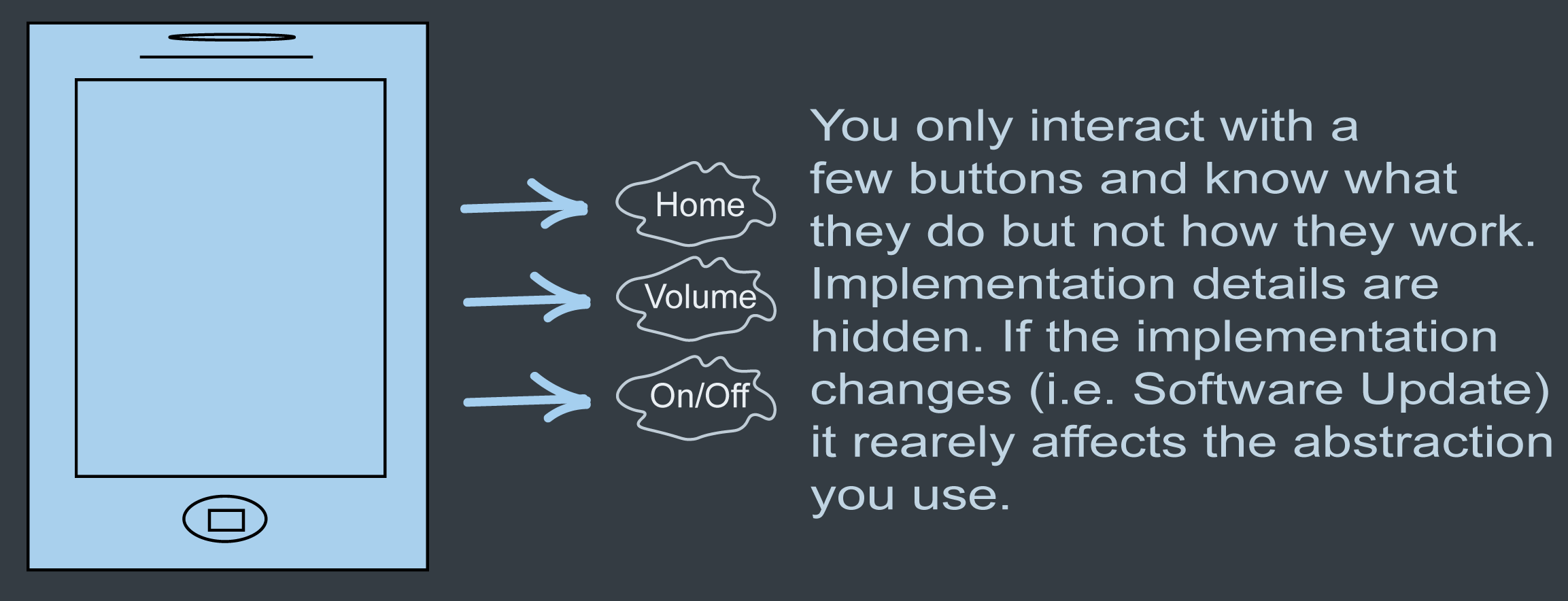
What is Abstraction
Abstraction is the process in which an object only exposes itself at a high-level, and hides its internal implementation details. Other objects that are calling this don't care how things are being implemented, they just need the information to be processed.
Think of this as a small set of public methods that any other class can call wihout knowing how they are actually being implemented behind the scenes.
Take the cell phone from the picture above for example. We don't know how the buttons on the phone are doing what they are doing, we just know what they do.
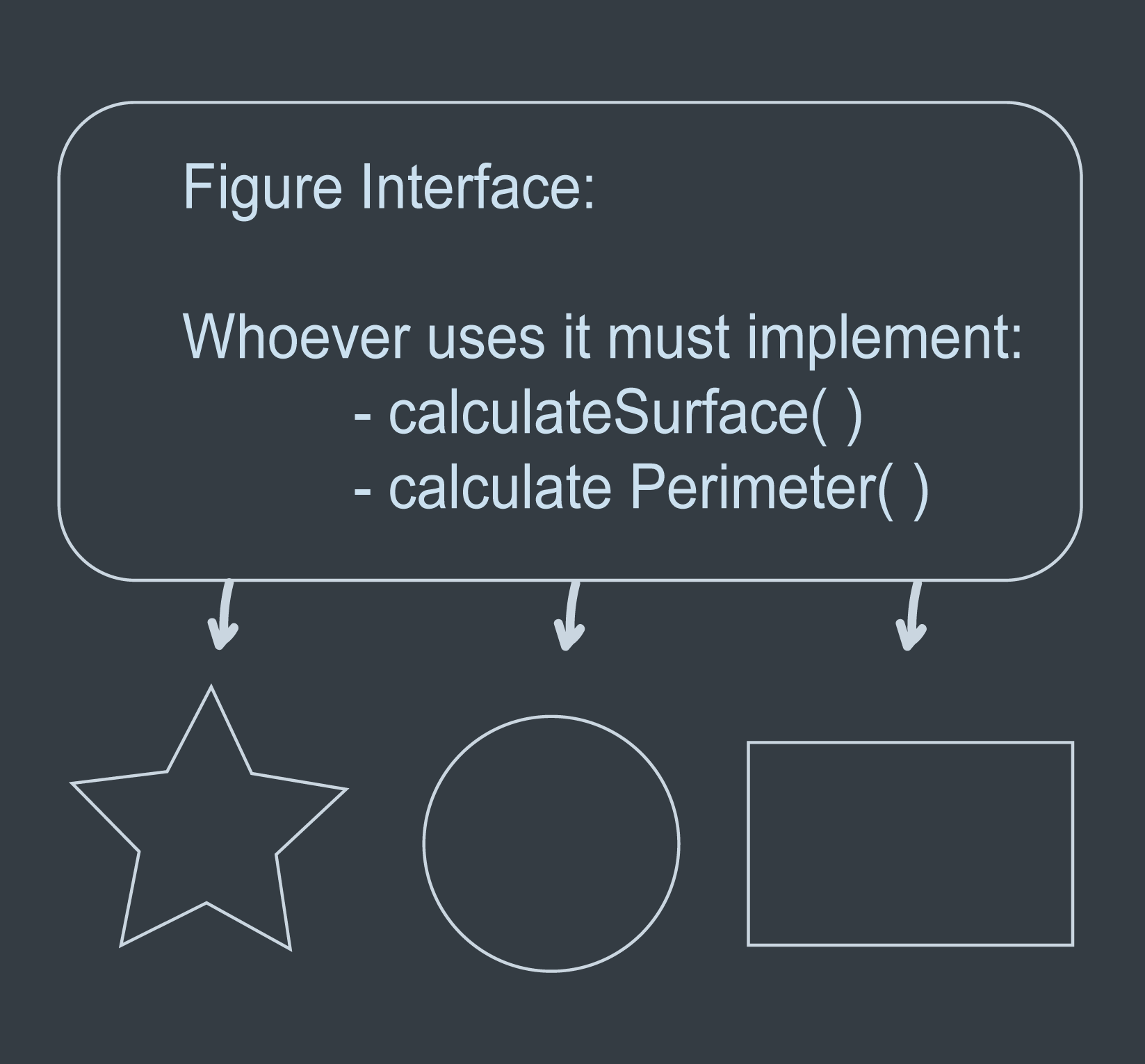
What is Polymorphism
Polymorphism means somthing occuring in multiple different forms. It allows objects of different types to be accessed through the same interface with each type implementing its own independent version of this interface.
The star, circle, and rectangle are all Figure's, they are just different types of figures. They all have a calculateSurface() and calculatePerimeter() method. The difference is how they are actually doing this calculation.
Now Thats All Folks
Thanks for taking the time to read this post! If you found it useful, or think others would enjoy it, share it!
If you found this post helpful, consider subscribing to my weekly newsletter I write to help developers level up and make more money!



Certainly! Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that revolves around the concept of “objects,” which can contain data in the form of fields (attributes or properties) and code in the form of procedures (methods or functions). Here are the fundamental concepts of OOP explained:
Class: A class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that all objects of that type will have. Think of a class as a cookie cutter, and objects as the cookies you create using that cutter.
Object: An object is an instance of a class. It is a concrete entity created based on the blueprint provided by the class. Each object has its own set of attributes (data) and can perform actions (methods) defined by its class.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation refers to the bundling of data and methods that operate on that data within a single unit, i.e., a class. It allows for data hiding, meaning that the internal state of an object is hidden from the outside world and can only be accessed through well-defined interfaces (methods).
Abstraction: Abstraction is the process of simplifying complex systems by hiding unnecessary details while highlighting essential features. In OOP, abstraction is achieved through classes and interfaces, which provide a simplified view of an object’s behavior without revealing its underlying implementation.
Inheritance: Inheritance is a mechanism that allows a class (subclass or child class) to inherit properties and behaviors from another class (superclass or parent class). This promotes code reusability and allows for the creation of hierarchical relationships between classes.
Polymorphism: Polymorphism means “many forms” and refers to the ability of objects to take on different forms or behaviors based on their context. In OOP, polymorphism is typically achieved through method overriding (providing a specific implementation of a method in a subclass) and method overloading (providing multiple methods with the same name but different parameter lists).
These concepts form the foundation of Object-Oriented Programming and are essential for building modular, maintainable, and scalable software systems. By leveraging classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, abstraction, and polymorphism, developers can create robust and flexible code that mimics real-world entities and relationships. zakbags.com/products/petit-sac-plat-small-flat-shoulder-bag-louis-vuitton
The star, circle, and rectangle are all Figure’s, they are just different types of figures.
Flexibility